Counterfeiters will use every method at their disposal to sell fakes, and learn key strategies from marketers to beat authentic brands to the top of search engine results.
- Black hat SEO are bad-faith methods of manipulating search engines
- Counterfeiters use these strategies to quickly rank highly on search engines to sell fakes
- Counterfeiters are known to use legitimate, paid-for advertising to boost their SEO
Search engine optimization (SEO) refers to a set of techniques used to improve a website’s or a page’s “organic” or “natural” (not paid-for) positioning on search engines. SEO is important for brands selling online as it greatly influences the amount of traffic that arrives at a website.
What is Black hat SEO?
Black hat SEO refers to a set of techniques that target only search engine results, rather than taking the human audience into account. The techniques involved can range from spammy to outright malicious, all of which go against the guidelines set out by the search engine. Black Hat SEO is used to quickly turn a profit on a website, rather than building a website intended for long-term use.
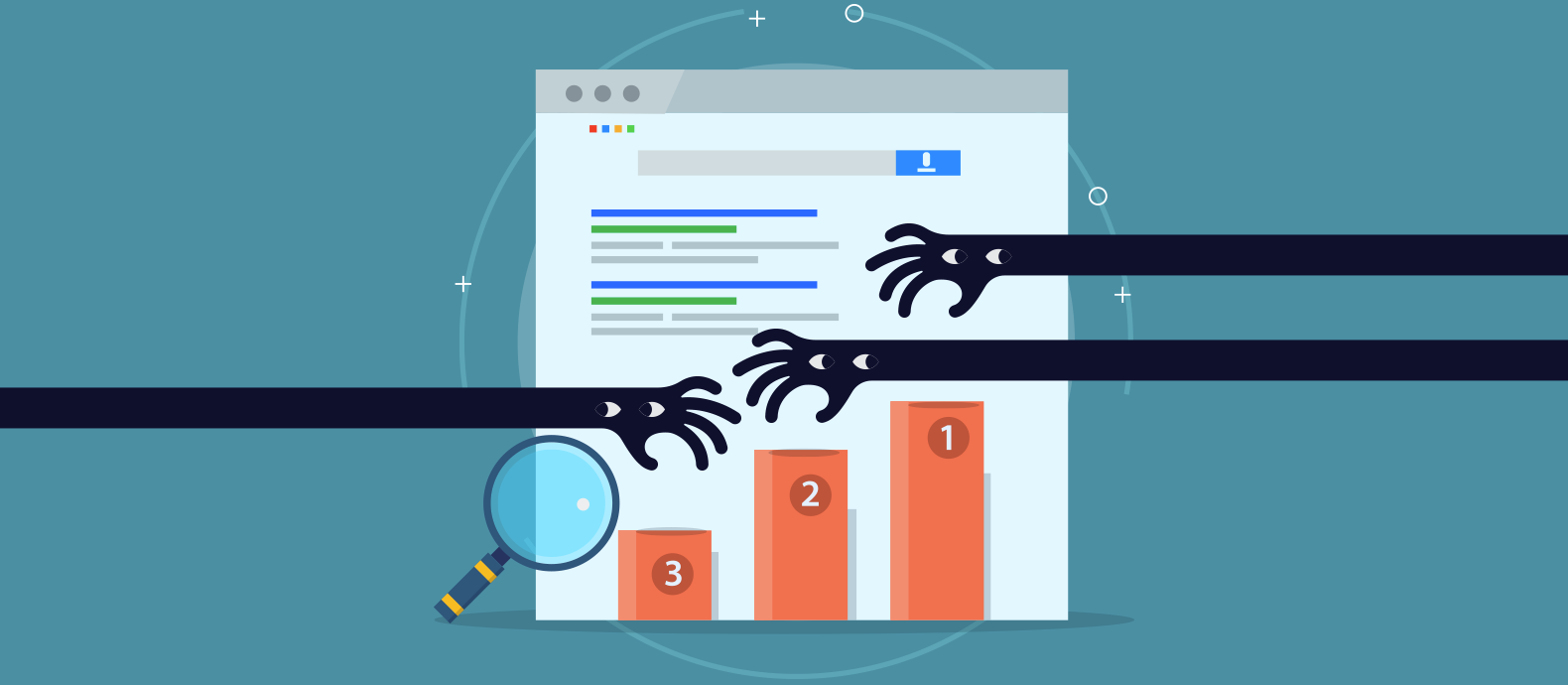
The image below is a prime example of how effectively black hat SEO can be used by counterfeiters. The page that a search for “cheap Real Madrid jerseys” brings up is listed entirely by counterfeit-selling websites for the first half of the page results, with only the final 5 organic results showing the authentic brand or legitimate resellers. The final result is a paid-for advert, purchased by an online marketplace that also lists fake Real Madrid jerseys.

Techniques of black hat SEO have been adopted widely, and to great effect, by counterfeiters in recent years. The fast turnaround of success that these strategies can bring makes them a perfect tool for counterfeiters, who also typically seek to set up shop and make a quick buck, rather than founding a respectable, or legal, business. Some of the most common black hat techniques used by counterfeiters include keyword stuffing, domain squatting, and redirecting doorway pages.
Keyword stuffing
Keyword stuffing is when a page is overloaded with keywords. The technique used to be much more effective and widely used before Google’s Panda and Penguin updates, though it can still well in the short term to draw enough traffic to sell fakes.
Counterfeiters in particular are adept at manipulating keywords to dodge brand protection, meaning their listings appear in user searches, but are often not caught by out-of-date anti-counterfeiting searches.
Invisible text is also used to compound the effectiveness of keyword stuffing – simply setting the text color to match the color of the background image, it can result in words visible to search engines, but not by human readers.
Domain squatting
Domain squatting, also known as cybersquatting, refers to the online usage of a third party’s trademarks in bad faith. It’s used to improve the infringer’s SEO positioning, to fool visitors into thinking the website is registered by the authentic brand itself, or to directly harm the real owner of the protected name.
Doorway pages
A doorway page is a single page, loaded with keywords and phrases to raise its positioning, that lead visitors to more a malicious page through on-page links, automatic redirects, or with fast meta refreshes.
The tactic is employed to great effect by counterfeiters, since the doorway page likely won’t infringe on intellectual property, and the linked pages will often be both difficult to find by bots, and easy to replace with a new ecommerce page if the original is taken down.
PPC
Pay-per-click advertising (PPC), is the marketing tool where adverts are placed on external websites and search engines, and the advertiser pays a fee for each click the ad receives.
PPC has become a larger issue within counterfeiting since 2009 when Google opened up trademarked keyword bidding on AdWords. What this meant is that any entity could pay to rank on searches of competitors’ trade names. Someone selling counterfeit running shoes could pay for Google Adwords’s results, so they appear for searches of “New Balance”, “Nike”, “Fila”, or any other authentic competing brand.
Keywords are auctioned off by search engines to the highest bidder, meaning if a brand doesn’t want third parties to rank for searches of their own brand, they have to pay to outbid them.
What can brands do?
Black hat SEO strategies, while eventually punished by search engines, are effective in the short run, and can pose a danger to the brands targeted by counterfeiters.
But fear not – as always, there are strategies that authentic brands can implement to counteract the damage caused by counterfeiters.
Protect your own brand name via PPC
Paying to rank for your brand name on search engines not only reduces counterfeiters’ ability to rip your brand off, but it will also help defend from legal competitors drawing traffic from your brand name to their website.
Enhance the safeguarding of your brand through PPC by engaging with a professional agency. Their expertise can fortify your online presence and protect against potential threats, ensuring a more effective and secure digital strategy.
Beat counterfeiters organically
Black Hat SEO doesn’t work as a long-term strategy. Websites employing these methods might get instant results and trick their way into a temporarily high listing, but SEs find out and punish the websites harshly for these strategies.
On the other hand, white hat SEO methods, which perhaps won’t bring immediate results to a website, will help to organically find a respectable site that climbs rankings over time, grows in domain ranking, and serves as a legitimate central hub for an online brand.
Reporting negative sites
All types of rogue websites can be reported and dealt with properly, first by sending a cease and desist (C&D) letter to the contact on the page, then another to the site’s content management system, then finally a third C&D to the domain host if the first steps fail to bring results.
It usually takes longer if you do all of the reporting actions by yourself. On the other hand, it’s very likely that the infringers will just ignore your takedown request. You might want to consider employing a professional third party who takes care of the takedown of negative websites for you.
What’s next
Black hat SEO methods, including keyword stuffing, domain squatting, doorway pages, and manipulating gaps in PPC content are widely used by counterfeiters to sell their fake products.
While search engines, such as Google, periodically release updates to curb the effectiveness of these dodgy tactics, they still tend to work in the short run to quickly boost the profile of their websites. With counterfeiters, that’s not enough to prevent them from adopting such methods – their business model is built on dishonesty and a quick turnaround of profit, so a delayed punishment on their search engine listings won’t phase them greatly.
Brands can counteract these measures by protecting their trademarked name on PPC by outbidding the counterfeiters, by founding a “white hat SEO strategy”, which relies upon gradual improvement and growth of content, and by reporting any bad-faith websites that may appear.