Red Points provides an overview of the key differences between utility patents and design patents when one should file a design patent or a utility patent application, and the application process for each kind of patent.
Summary:
- What is a utility patent vs a design patent? A utility patent protects the functional aspects of an article, i.e., the way the article works and is used, whereas a design patent only protects the ornamental appearance of an article, such as its shape, configuration, and/or surface ornamentation.
- When to file a design patent vs utility patent application? A design patent application should be filed when seeking protection for the unique exterior appearance of an article. When seeking protection for the way an article functions including its mechanical structure or the way the article is used, a utility patent application filing is appropriate.

I. What is a Design Patent vs Utility Patent?
(i) Utility vs Design Patent Examples
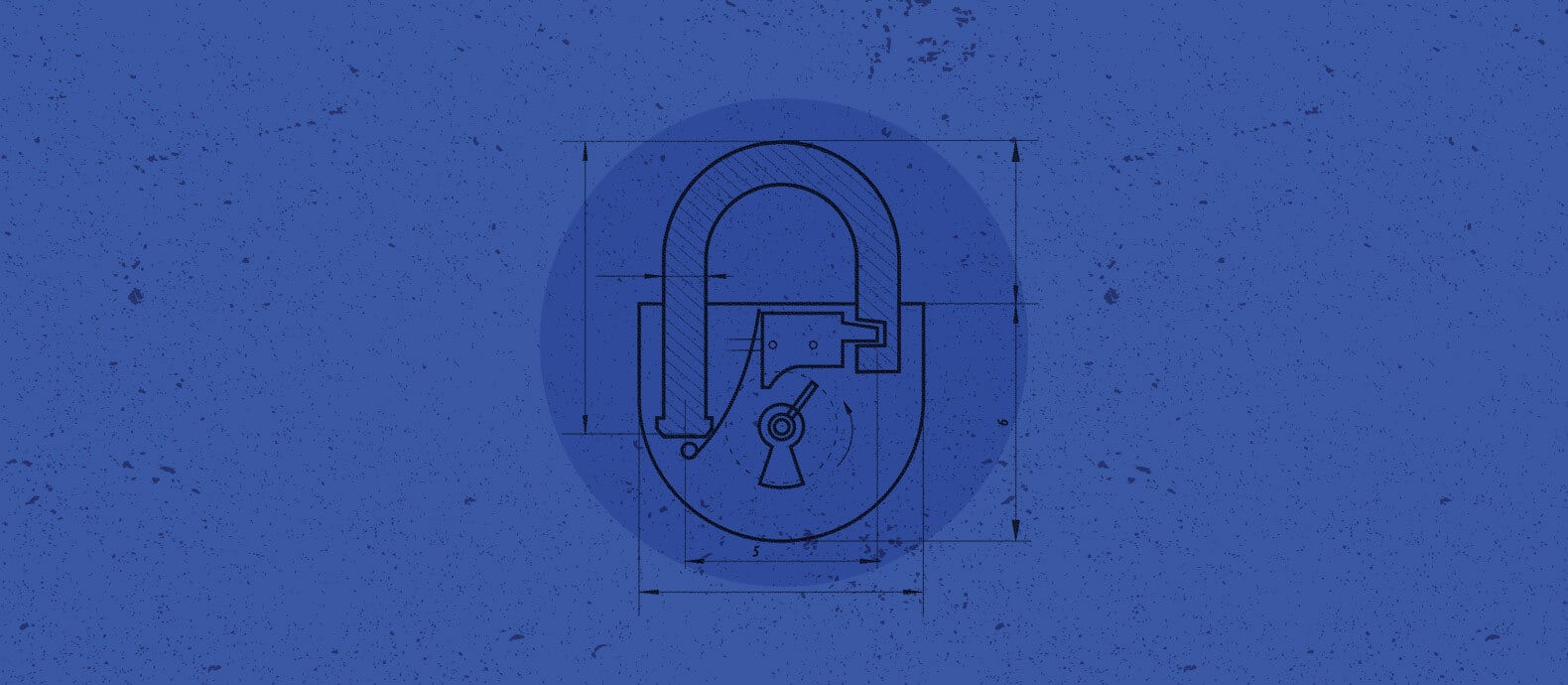
A design patent protects the original ornamental appearance of an article, such as the configuration or shape of the article (e.g., round, cylindrical, etc.) and/or surface ornamentation (e.g., the pattern of indents, ridges, etc.) applied to the article.
A design patent only protects the exterior visual appearance of an article. A design patent application cannot be filed for a hidden or interior design of an article because hidden designs, by nature of not being visible, cannot be ornamental in nature. Similarly, functional mechanical structures are not ornamental in nature and cannot be protected by design patents.
In contrast, a utility patent protects the way an article functions and/or the way the article is used. A utility patent protects an invention that is novel, non-obvious, and useful and that falls under at least one of the following four categories:
- Process: Process claims are directed to methods of performing an action or a series of actions. The subject matter of method claims can be highly diverse, e.g., methods of treating diseases, methods of performing an algorithm to protect software functioning, methods of using devices, etc. can all be claimed in utility patents.
- Machine: Machine claims are directed to devices or combinations of devices in systems.
- Article of manufacture: Includes claims directed to articles that are manufactured such as ceramics, chairs, shoes, etc.
- Composition of matter: Composition claims are directed to chemical compositions (e.g., the chemical structure of a small molecule, a pharmaceutical composition of a combination of ingredients, etc.) or biological compositions (e.g., nucleic acid sequences, amino acid sequences, antibodies, etc.)
(ii) Utility Patent vs Design Patent Key Differences
A utility patent protects the functional aspects of an article, while a design patent only protects the ornamental appearance of an article.
A utility patent is harder and takes significantly longer to obtain (typically 3-5 years) than obtaining a design patent (about 1-2 years). Consequently, obtaining a utility patent is more expensive than obtaining a design patent.
Given the expense and complexity of obtaining a utility patent, it is highly advisable to perform a patentability search prior to filing a utility patent application. The purpose of this is to search for previously published patents, patent applications, or other publications similar to the invention to be patented for assessing novelty and non-obviousness.
How long does a utility vs design patent last?
A utility patent is valid for 20 years from the date the application is filed. A design patent in the United States is valid for 15 years from the date the design patent application is granted.
Unlike utility patents that are subject to payment of periodic maintenance fees to prevent them from expiration, design patents, once granted, do not require payment of maintenance fees. For more detailed information on utility patents, read Red Point’s Ultimate Guide to American Utility Patents.
II. When to File a Design Patent vs Utility Patent Application?
When the article in question has a unique exterior appearance and competitors are likely to copy its appearance, a design patent application should be filed. Design patent applications are commonly filed to protect aesthetic features of consumer goods such as mobile phones, shoes, cars, etc.
However, when seeking protection for the way an article functions, including its mechanical structure, whether on interior or exterior surfaces of the article, or the way the article is used, a utility patent application filing is appropriate.
Both design patent application and utility patent application should be filed if protection is desired both for the aesthetic appearance of the article as well as its functional aspects.
III. How to File a Design Patent vs Utility Patent Application
A utility patent application must include a description of the invention and a claim set. Drawings may be included, if necessary, to understand the invention. A design patent application must include drawings of the ornamental appearance of the article, a description of the drawings and the ornamental appearance of the article, a single claim, and a brief description of the article and its intended use.
Drawings in design patent applications must use solid lines for the claimed ornamental features of the article and, if necessary, broken lines for the visible unclaimed environmental structure in which the claimed ornamental features are found. Fees for filing, search, and examination also must be included in both utility and design patent application filings.
Design and utility patent applications can be filed at the national patent offices of each country in which patent protection is sought. International utility and design patent applications simplify the process of obtaining patent protection in different countries by allowing the filing and processing of a single application, which can then be subsequently pursued in countries in which patent protection is desired.
International utility patent applications can be filed under the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) by filing PCT applications, whereas international design applications (IDAs) can be filed for design patent applications. Once your patent is registered, staying proactive is the best way to prevent others from stealing what you have achieved.
To find out more about how Red Points’ brand protection software can help you safeguard your revenue by protecting your design patent, get in touch and request a demo today.