For brand protection, it’s important to know why consumers actively choose counterfeits over authentic goods. The answer is more nuanced than a simple difference in price.
- Choosing to buy counterfeits is largely a battle between moral values and saving money
- Luxury goods can be a reward for success, or a ladder to success themselves
- Brands should focus on educating their customers about the harms of fake goods.
It’s easy to look at the popularity of counterfeit products and to say it’s just down to consumers bargain hunting. But there are nuanced factors that have an influence on a consumer’s decision to buy a counterfeit or not, including cultural factors and cognitive dissonances within consumers.
For this article, we’ll be looking at non-deceptive counterfeits. What this means is the consumer is aware the product they are purchasing is an illegal replica of an authentic brand. This is in contrast to deceptive counterfeits, which rely on tricking consumers into believing they represent the real brand, and are selling an authentic product. It only makes sense to look at consumer opinion if the consumer is fully aware of the product they are buying.
It depends on the product
Counterfeiting, piracy and other forms of intellectual property infringement cover an enormous range of products. It’s very unlikely then that consumers would have consistent views regarding such a diverse scope of crimes.
One of the clearest factors is the luxury aspect of certain products, especially within fashion. An important aspect of high-end fashion is not just the popular, elegant design of an item, but also the value a consumer sees in wearing prestigious labels. Products like these are huge status symbols. Walking around a city with Gucci or Prada clearly visible to other people is in itself valuable to people, as these products meant to reflect the class and social standing of its wearer. Consumers who knowingly purchase counterfeit products of high-end fashion brands find it worthwhile to buy products that are lower quality, be that in terms of the material used, the manufacture process, or other factors, if they feel they’ll still experience the “prestige effects” of being seen in Armani or Louis Vuitton products.

Contrast this against clothing whose value is in the function, such as outdoor apparel. Brands in industries such as these create demand for their products by consistently producing items that are reliable in extreme and potentially dangerous weather conditions and climates. Consumers are willing to pay more for these products as they’ve placed trust in the brands, and understand this type of clothing can help keep them safe in the great outdoors.
Piracy is particularly troublesome, especially with software, and torrenting is growing again. It’s often the case that there is zero difference in quality between a paid-for download and an illegal download. The files are copied exactly and redistributed as clones of their original form. These products are purely functional, and don’t act as status symbols. In an isolated comparison, there’s little incentive for consumers to pay full price for software of copyrighted content if there’s also a free or heavily discounted version available to them.
Personality factors
However, the choice to purchase a counterfeit item is not as simple or cold as a pure analysis as described above. There are other influences in play, and certain personality traits are extremely important. This section largely comes from the research paper The Devil wears (counterfeit) Prada, a study into Chinese consumer attitudes towards luxury brand counterfeiting.
Value-consciousness
Value-consciousness refers to the importance an individual places on the price of products when making consumer decisions. In short, the cheaper they can find a product for, the better. Consumers who are especially value-conscious are prone to more a more positive attitude towards counterfeit products.

Integrity and a sense of justice
Consumers’ personal sense of justice, adherence to law and their ability to stick to a set of moral values play a considerable part in their choice to buy fake goods. As taking part in counterfeiting is an unethical activity, considering the range and depths of economic and social harms counterfeiting causes, consumers who value their integrity and have a strong sense of justice will be hugely put off by the idea of purchasing fake products.
Personal gratification
The need for a sense of accomplishment and the ability to consume luxury products is known as personal gratification in this context. Individuals who strongly embody these values would theoretically also revere acquiring authentic brands over counterfeits. They are unlikely to accept inferior-quality products such as counterfeits, as they are looking for the full experience of luxury products and satisfaction of owning them. A knock-off that may look similar enough to the original to fool peers doesn’t grant this effect.

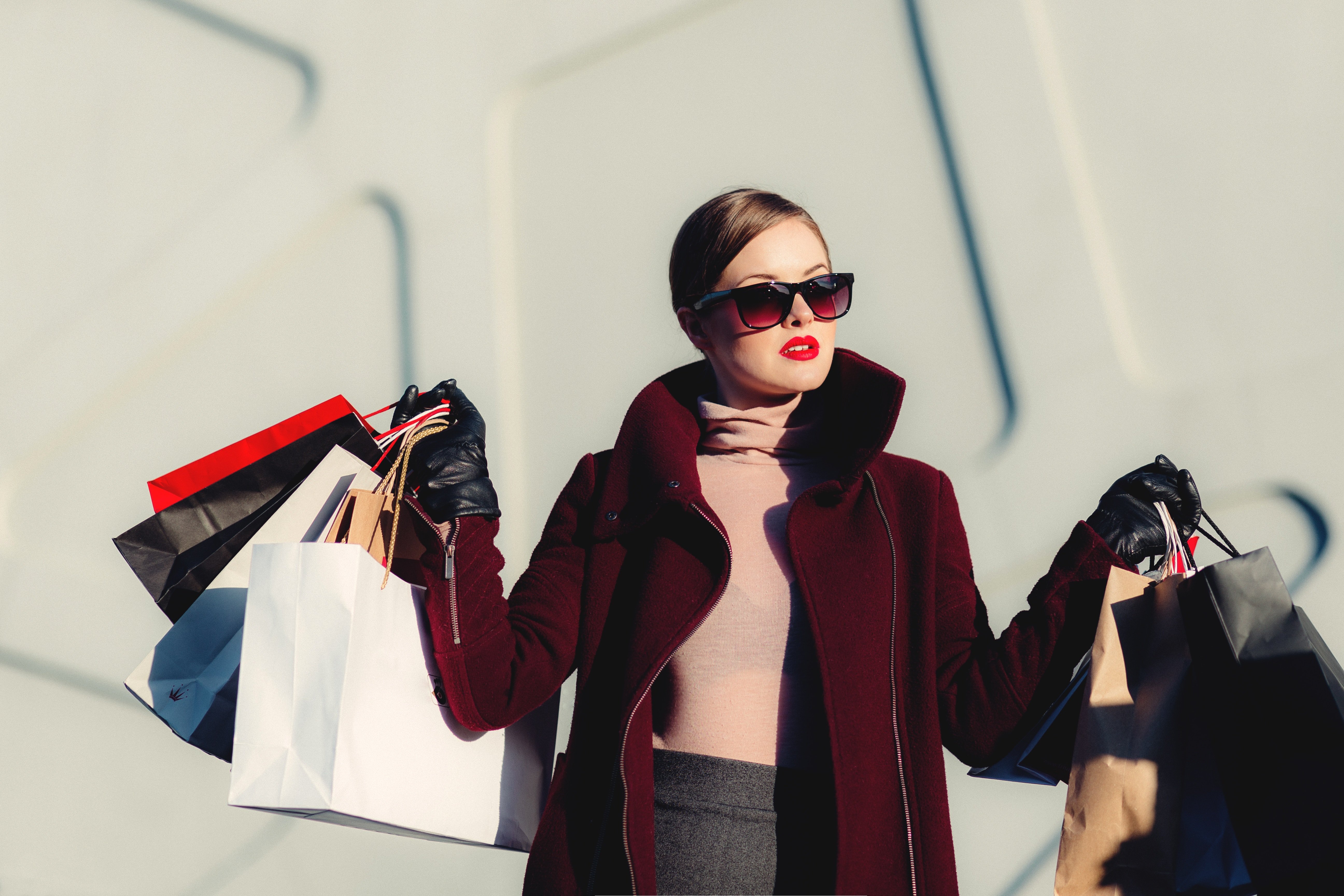
Status consumption
Social status is an important concept in every culture. This is especially true of China, where face, sociological term for an individual’s public self-image, is a core aspect of a person’s position in society. For people driven towards status consumption, public displays of their own accomplishments, such as showing to the world that they own impressive, high-end products, is an important aspect of social positioning.
The idea of being discovered for consuming counterfeits is deeply unpleasant for status consumers, as it may reveal them as being in a lower social rank than they had displayed. However, counterfeits could function as a shortcut for social climbing – without really being able to spend money on expensive, prestigious items, individuals could gain the same social benefits without being at a high level economically.

Novelty-seeking
The final influential personality factor is novelty-seeking. As readers may guess, this is the drive for individuals to continually consume new products. Novelty-seeking as a personality attribute drives consumers to products with low purchase risk – they are less likely to invest heavily in single items, as they’d rather have a series of new products than a single item. Individuals such as these would have a more positive attitude towards counterfeits, since they are a cheap way of satisfying curiosity of products and their need for experimentation.
Takeaways for brands
The technology used in product manufacture is constantly improving, and many are becoming more affordable. This is great news for counterfeiters – the items they make are becoming higher quality, and more similar to the original item as time goes on. This is particularly influential for people with status-consuming attributes. If a counterfeit can provide the same influence to social standing and face as the authentic product, with a near-zero risk of discovery from peers, then the risks are hugely mitigated and consumers may be more motivated to purchase a counterfeit.
What this means for brands is that they cannot afford to rest on their laurels and trust that the superior quality of their products protects them from ruin by counterfeits.
Taking these findings into account, a solution for discouraging consumers from purchasing counterfeits appears. Consumer education can be wielded to great effect to help people understand the true social harms the black-market industry causes. When consumers grapple with the balance between value-consciousness and their sense of justice, reminding them of the harms caused by counterfeiting, including causing mass loss of employment, refugee enslavement and links to terrorist groups, this can influence them away from supporting illegal activity. After all, the more consumers know about the damage done by counterfeiters, the harder they find it to rationalise purchasing fake products.
Photos by Fancycrave, freestocks.org, PaalHarald, and Becca McHaffie.