Fake websites are a problem for online businesses and consumers daily. In the last quarter of 2022 alone there were around 1.35 million unique fake URLs online. Among these counterfeit websites, a significant number contained misleading, malicious, and dangerous content.
Google holds over 90% of the worldwide search engine market share and the top-ranking page in Google’s organic search results has an average click-through rate (CTR) of 27.6%. Therefore online businesses need to be aware of how duplicate or fake websites may be impacting their visibility and profitability on Google.
When fake websites rank alongside or above the websites of legitimate brands they damage their business’s ability to reach customers, market products, and grow online. In such cases, you need to know how to remove a website from Google and protect your business’s online presence. Learning how to take websites off Google can also help you rectify a variety of issues with your own business’s website.
Below, we’ve explored a variety of topics that will help you learn how to remove a website from Google, including:
- Why remove a website from Google?
- What’s Google’s policy on fake websites?
- How to remove a website from Google: Step-by-step guide
- Dealing with multiple fake websites on Google?

Why remove a website from Google?
Google processes user searches by creating a shortlist of web pages based on the search topic. In an instant, Google will analyze the content of each listing including text, images, and video files. The pages will then be ranked from most to least relevant, using the content of the site as well as a combination of other information like location, language, device, and previous browsing behavior. Scammers can create fake websites to take advantage of these processes and outrank legitimate websites.
These websites can function in a variety of ways. Commonly, malicious websites will mimic legitimate high-ranking sites to trick people into clicking on them and engaging in their scams. Fraudulent websites may also sell counterfeit copies of your products, steal your intellectual property (IP), and seek to take advantage of unwitting browsers with malware.
If a fake website ranks highly on the Google SERP it will be taking attention away from your business’s website. Equally, scammers can include backlinking within their fake business websites to drive more traffic to them because Google will interpret the website as having value. In short, you may want to remove a website from Google for the following reasons:
- To stop fake websites from using your business’s IP – If you allow others to exploit your IP your brand will lose value and you may have to pursue legal routes. By removing an infringing website from Google you will protect your assets and ensure your business has a strong online presence. Also, you will prevent your potential customers from becoming victims of scammers looking to steal their sensitive and financial information.
- To remove wrong, misleading, or outdated information – Some websites may display information about your business that is wrong or confusing. By removing such websites you will ensure customers can trust what they see online about your business.
What’s Google’s policy on fake websites?
To be eligible to appear in Google web search results a website must abide by Google’s content and spam policies. Google can detect fake, and policy-violating, websites through both automated and human review systems. If websites violate Google’s policies they will rank lower in their results or not appear in the results pages at all.
Google’s main search content policies concern:
- Highly personal information
- Exploitation material or imagery
- Webmaster and site owner requests
- Valid legal requests
- Spam
Their policy on infringing websites is largely contained in their policies against spam. Based on their policies, the following practices and behaviors, often associated with fake websites, can lead to demotion or removal from Google:
- Cloaking – presenting different content to users and searching to manipulate search ranking and mislead users.
- Doorways – creating sites or pages for specific, similar search queries that direct users to intermediate pages that do not contain the information the user is looking for.
- Hacked content – content placed on a website without permission. Scammers can inject malicious code and web pages into existing sites.
- Hidden text and links – placing content on a fake website that is hidden from human visitors but used to manipulate search engine algorithms.
- Keyword stuffing – filling a website with keywords or numbers to manipulate Google Search result rankings.
- Link spam – scammers will use links, similar to keywords, to manipulate Google search rankings. This occurs with both outgoing links within the site and links to their fake website from other web pages.
- Machine-generated traffic – bad actors will send automated queries to Google and use technology to check Google Search rankings. These activities consume resources and interfere with Google’s normal processes.
- Malware and malicious behaviors – infringing websites are often host to malware or unwanted software, installed by scammers to take advantage of visitors.
- Misleading functionality – services and functionality that trick users into thinking they can access content that is inaccessible or broken.
- Scraped content – some fake websites use “scraped” content from legitimate and reputable sites to populate their pages. This is done to manipulate search rankings and trick users. In some cases, this method may also constitute copyright or trademark infringement.
- Sneaky redirects – sending a visitor to a different webpage than the one originally requested.
- Spammy auto-generated content – content that is generated programmatically that contains nothing original or of sufficient value to a website visitor.
How to remove a website from Google: Step-by-step guide
If you find a website that you believe is violating your intellectual property or infringing one of Google’s content policies, you can report that site to Google and get it removed. You can either report it as a non-legal policy violation or as a legal violation related to intellectual property or privacy.
Here is a step-by-step guide to help you learn exactly how you can report a website on Google via both processes:
Policy violation
Step 1: Select the reason you wish to report content. If it is malicious intent then choose either Malware, Phishing, or Spam.
Step 2: After selecting a reason you will be redirected to a Google Search Central page.
Step 3: Provide the page URL and select what is wrong with the webpage.
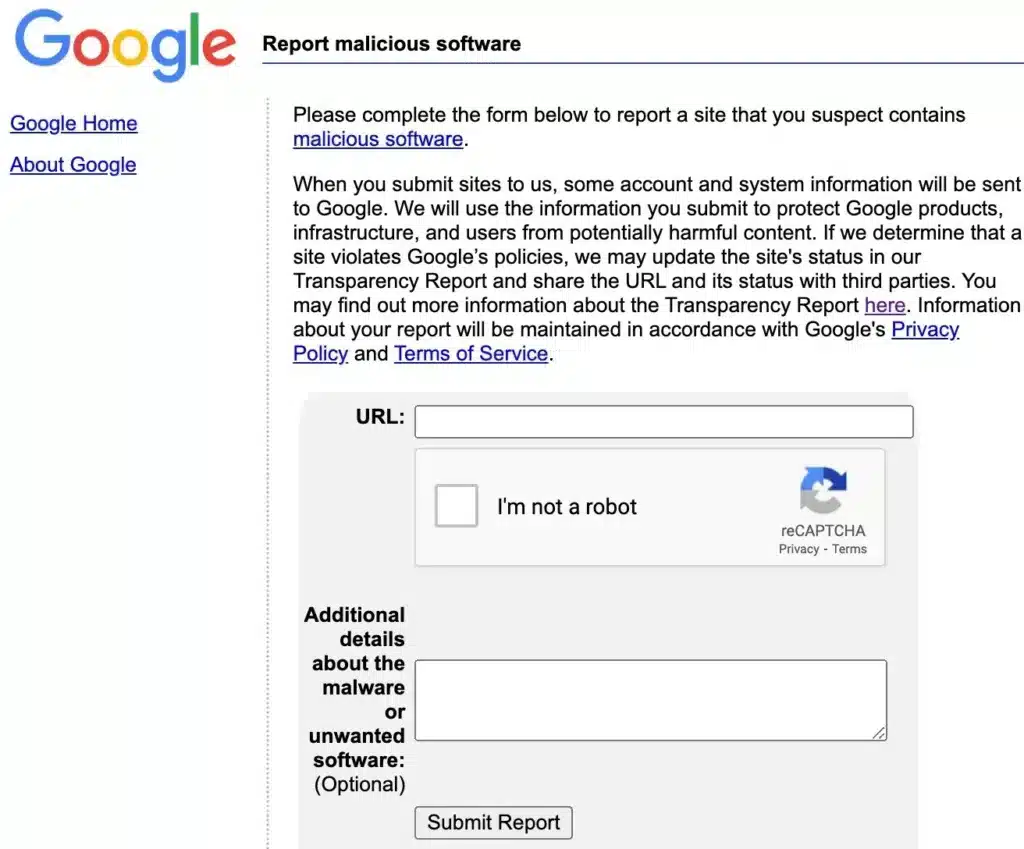
Step 4: Provide further details by selecting the appropriate category. Include all the pertinent evidence against the page and then submit your report.
Legal violation
Step 1: Select the reason you wish to report content.
Step 2: Select the type of Intellectual Property infringement you believe has occurred.
Step 3: State whether you are the IP owner or whether you are authorized to act on their behalf.
Step 4: Select the type of infringing work that you have seen on the website.
Step 5: Create a request. You will then be redirected to Google’s IP Removal Request page.
Step 6: Here provide the relevant details about your business, your IP, and the URL of the website containing the infringing material.
Step 7: Affirm the sworn statements and provide a signature for the form.
How to detect fake websites
You can detect fake websites by conducting your own manual searches via Google. Through keyword and image searches, you can identify websites that may be using your copyrighted material without permission. If you believe that just one or two fake websites are impacting your businesses then you can seek to manually file complaints yourself. This can be an effective strategy when dealing with a limited number of cases.
However, website impersonation and online scams are rarely isolated incidents. If many websites are infringing your brand’s intellectual property then it quickly becomes very difficult for you to manually monitor and remove them with any efficiency. In such incidents, we recommend using a specialized automated solution to give your business a helping hand.
How to deal with multiple fake websites on Google
Manual takedown requests are not an efficient or cost-effective way to tackle multiple fake websites on Google. If you work via manual methods some of those websites will inevitably slip under your radar. In addition, you will be using up the valuable time and resources of your business without any guarantee of results. However, there is a worthy alternative.
Red Points’ Search Engine Removal Services is the ideal automated solution to help your business find, report, and remove multiple fake websites on Google. Here’s how it works;
- Find
Our bots crawl search engines like Google every 15 minutes. With automation and machine learning technology we can review thousands of potential infringements in the time it may take for you to conduct a single manual review.
We can identify IP infringements and policy violations with speed which will allow you to catch any scammers and bad actors that may have previously slipped under the radar.
- Remove
Then we can help you begin the removal process by instantly reporting to the search engine for delisting. Our bots will identify and monitor the listing’s URL to regularly check the status of the infringement.
We will continue the removal process by sending a DMCA takedown request automatically to any infringing websites to ensure the owners remove the illegitimate content.
- Measure
It is important to understand how you can continue to evolve your brand protection actions. With Red Points’ solution, you have access to performance dashboards and reports.
These tools will help you calculate the economic impact of your actions. This in turn will allow you to improve your business’s approach to fake websites and the way you deal with IP infringement.
With an excellent 99% average success rate from detection to removal and an average takedown time of 1.5 days, clients like Puma, Hugo Boss, and FILA have trusted Red Points to help them tackle infringing online content.
What’s next
It is important to act against malicious websites as soon as possible. The quicker you act the easier it will be to protect your business from languishing at the bottom of Google’s results pages. Swift action will allow you to mitigate the impact of those websites and establish strong connections with your online customers.
1.4 million fake websites are created every month just for phishing purposes. This constant wave of illegal and malicious activity can be difficult to tackle alone. That’s why using a specialized automated solution to detect and remove fake websites can be vital to your business’s online success.
Automation will improve your speed, reach, and precision enabling you to stay on top of the issue and focus your products or services. To learn more about how Red Points can help you remove a website from Google, talk to one of our experts here.