According to the 2020 Internet Crime Report, global losses due to cybercrime reached $13 billion over the previous five years. Cybercrime costs are expected to rise 15% annually, reaching $10.5 trillion by 2025. So with online threats on the rise, understanding the differences between spoofing and phishing is crucial for both businesses and individuals alike. In this article, we will explain the key differences between spoofing and phishing, and why raising awareness and taking proactive measures are key to protecting your digital assets. After all, the more you know about different kinds of cyber threats, the less likely you and your customers are to fall victim to them.

What is spoofing?
Spoofing is a type of cyber attack where a person or program disguises as another by falsifying data. This is done to deceive victims, steal their information, or spread malware. The focus of spoofing is to realistically impersonate a trusted source so that other types of cyber attacks like phishing are more believable and can be carried out more effectively. Understanding the different kinds of spoofing can help you identify and prevent attacks on your business before they cause any harm.
Types of spoofing
- Email spoofing: Attackers send emails that look like they come from a trusted source, often with the intent to steal sensitive information or spread malware.
- Caller ID spoofing: The attacker manipulates the caller ID so that the victim’s phone displays a trusted name or number, tricking the recipient into answering the call into believing they are speaking to a legitimate person or business.
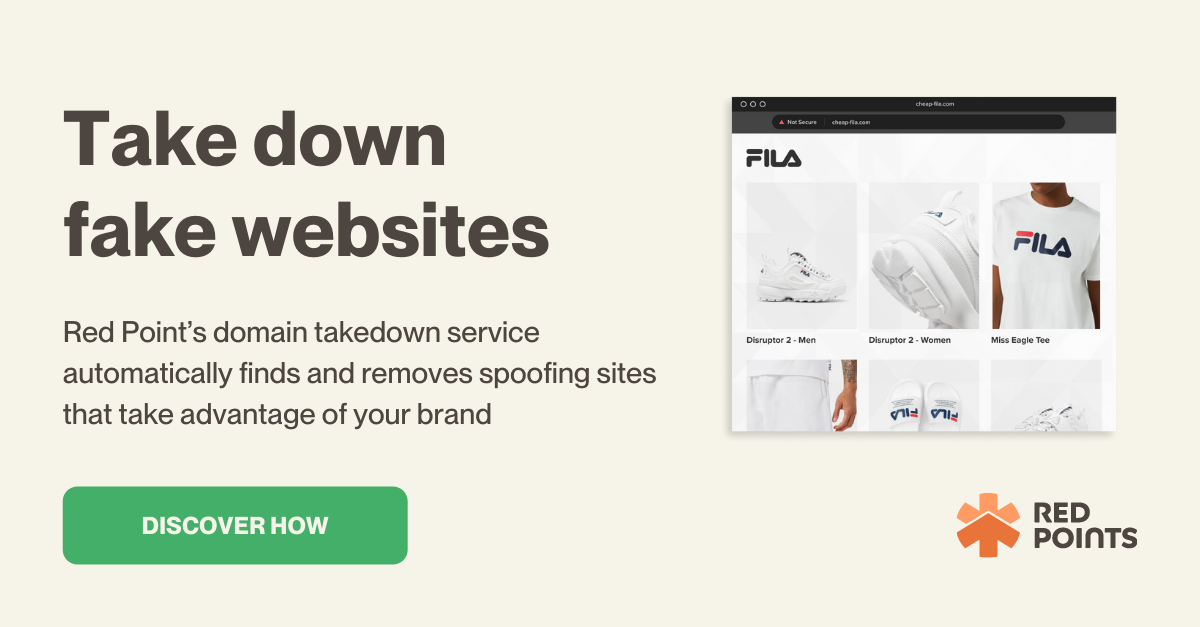
- Website spoofing: Attackers build a fake website, which is created to look like a legitimate one, tricking users into entering their personal or financial information.
- IP spoofing: Attackers forge the IP address of a device, making it appear as if it is coming from a trusted source.
How spoofing works
Imagine a situation where a cybercriminal creates a website that looks almost identical to your company’s official site. They then send an email to your customers, appearing to be from your company, directing them to this fake website. Once the customer is on the site, they may unknowingly enter their login details, which are then captured by the cybercriminal.
It’s an easy trick to fall for – especially as cybercriminals are getting ever better at replicating legitimate websites.
How to spot a spoofing attack
- Unusual email addresses that do not match the sender’s usual address.
- Unexpected requests for personal information or taking urgent actions.
- Inconsistent URLs that seem slightly off or have subtle differences from the legitimate ones.
- Grammar and spelling errors, which are often the quickest and easiest way to spot a fake website or email address.
- Unusual caller IDs that show trusted names or numbers but come at odd times or with strange requests should be treated with suspicion.
What is phishing?
Phishing refers to a type of cyber attack where fraudsters use deceptive emails, messages, or websites to trick individuals into sharing sensitive information like passwords, credit card numbers, or personal identification details. A phishing attack may begin with spoofing as the attacker aims to impersonate the trusted source that they want you to reveal your personal information. Recognizing these signs can help you avoid falling victim to phishing attacks and keep your personal and business information secure.
Types of phishing
- Email phishing: The most common form of phishing, where attackers send emails that appear to be from legitimate sources. They generally contain content urging recipients to click on malicious links or download infected attachments.
- Spear phishing: This is a more targeted approach, where attackers personalize their messages to a specific individual or organization, making the deception appear more convincing.
- Whaling: A form of spear phishing that targets high-profile individuals, such as executives or celebrities, with the intent of stealing sensitive data or gaining access to privileged systems.
- Smishing (or text phishing): Phishing attacks that are conducted via SMS, where attackers send text messages containing malicious links or prompts for personal information.
- Vishing (or caller ID phishing): Voice phishing, where attackers use phone calls to impersonate trusted people or businesses, and trick victims into sharing personal information.
How phishing works
Have you ever received an email that looks like it’s from your bank or another trusted business, but subtle inconsistencies give it away? Then you’ve received a phishing email. Usually, these emails will warn you of something that requires immediate action, like unusual activity on your account. It relies on your panic at the moment, meaning that you don’t take time to consider whether this could be real or fake, and urges you to click on a link to verify your details. This link will lead you to a fake website that looks identical to your bank’s official site. Once you enter your login details, the attackers will capture this information and gain access to your real bank account.
How to spot a phishing attempt
- Look out for suspicious email addresses that don’t match the legitimate sender’s domain.
- If the email uses urgent or threatening language that creates a sense of urgency or fear, it might push you to act quickly without thinking.
- Unexpected attachments or links should be treated with caution, especially if they prompt you to enter personal information.
- Phishing emails often use generic greetings like “Dear Customer” instead of your actual name.
- Many phishing attempts contain noticeable grammar and spelling mistakes.
- Emails offering prizes, rewards, or unbelievable deals are often phishing attempts. Remember: if it seems too good to be true, it probably is.
Key differences between spoofing and phishing
Understanding the differences between spoofing and phishing and the intent behind each type of attack can help you better protect your digital assets. You can use this information to help develop an effective cybersecurity strategy that’s one step ahead of the fraudsters.
| Aspect | Spoofing | Phishing |
| Definition | Disguising a communication from an unknown source being from a known, trusted source. | Using deceptive emails, messages, or websites to trick people into sharing sensitive information. |
| Intent | To deceive and manipulate trust to carry out identity theft, steal data, or spread malware. | To trick recipients into sharing personal information or clicking on malicious links. |
| Techniques Used | Email spoofing (altering the sender’s email address to make it appear as if it’s coming from a trusted source) Caller ID spoofing (changing the caller ID to display a trusted name or number) Website spoofing (creating a fake website that looks like a legitimate one to trick users into entering sensitive information) IP spoofing (forging the IP address of a device to make it appear as if it is coming from a trusted source) | Email phishing (sending deceptive emails that appear to come from legitimate sources) Spear phishing (crafting personalized messages targeting specific individuals or organizations to make the deception more convincing) Whaling (targeting high-profile individuals with personalized attacks) Smishing (phishing attacks via SMS) Vishing (using phone calls to carry out phishing attacks) |
| Communication Channels | Email, phone, websites, IP addresses | Primarily email, but also SMS (smishing) and voice calls (vishing) |
| Target | Any communication channel | Primarily email users, but also targets via SMS and phone calls |
| Scope | Can occur independently or be part of a larger attack | Often includes elements of spoofing as part of a broader strategy |
Real-life cases of spoofing and phishing
Understanding the real-world impacts of spoofing and phishing highlights the importance of strong cybersecurity measures. There are a number of recent statistics and notable cases that highlight the financial and data loss impacts of these attacks.
Statistics on financial and data loss impacts
- Financial losses: The FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) reported that in 2020, businesses and individuals lost over $1.8 billion to phishing attacks alone.
- Data breaches: According to the 2021 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, phishing was involved in 36% of data breaches, highlighting its significant role in compromising sensitive information.
- Business email compromise: BEC is a form of email spoofing that resulted in over $2.4 billion in adjusted losses in 2021, making it one of the most financially damaging cybercrimes.
Notable cases of spoofing
- In 2021, Barclays Bank faced an email spoofing attack where cybercriminals impersonated the bank’s official email addresses to send fraudulent emails to customers, attempting to steal personal and financial information. This resulted in Barclays customers seeing millions of pounds vanish from their bank accounts.
- Credit rating agent Equifax experienced a spoofing attack in 2017 where attackers used spoofed email addresses to trick employees into divulging sensitive information, contributing to a massive data breach that affected 147 million people.
Notable cases of phishing
- Between 2013 and 2015, a Lithuanian hacker conducted a phishing scheme against Facebook and Google, tricking employees into wiring over $100 million to fraudulent bank accounts by posing as a legitimate hardware vendor.
- In 2014, Sony Pictures fell victim to a sophisticated phishing attack that led to a massive data breach. Hackers gained access to sensitive employee information, unreleased films, and confidential company emails, resulting in significant financial and reputational damage.
Automated solution for spoofing attacks
To combat the ever-growing threat of spoofing, businesses need robust, automated solutions. Red Points offers a powerful Domain Takedown solution that can help protect your brand against fraud by identifying and removing fake domains quickly and efficiently.
How Red Points works
- Detection
Our advanced technology scans the internet for suspicious domains that copy your brand. This continuous monitoring ensures that new threats are identified as soon as they appear.
- Validation
Our system validates the infringements by analyzing a variety of factors you specify, such as a domain’s registration information and website content. This validation can be automated based on rules or you can request the enforcement manually.
- Removal
After validation, we initiate the takedown process. Without analyst hours, our technical teams work swiftly to remove the fraudulent domain, minimizing the potential damage to your brand and customers.
- Analysis
We provide comprehensive reports on the actions taken, the threats mitigated, and the overall impact on your brand’s security. This allows you to understand the effectiveness of our protection and can be used to boost and develop your brand protection strategies.
What’s next
Understanding the differences between spoofing and phishing is essential for protecting your business from cyber threats. While phishing often targets individuals to steal personal information, spoofing attacks aim to deceive victims by impersonating trusted sources, which has the potential to cause significant financial and reputational damage.
Red Points offers a comprehensive set of tools to help safeguard your brand against these threats. Our Domain Takedown solution is designed to detect and eliminate fraudulent domains quickly so that your brand remains secure.
Request a demo today, and you can see firsthand how our technology can protect your business from spoofing attacks and maintain your brand’s integrity.